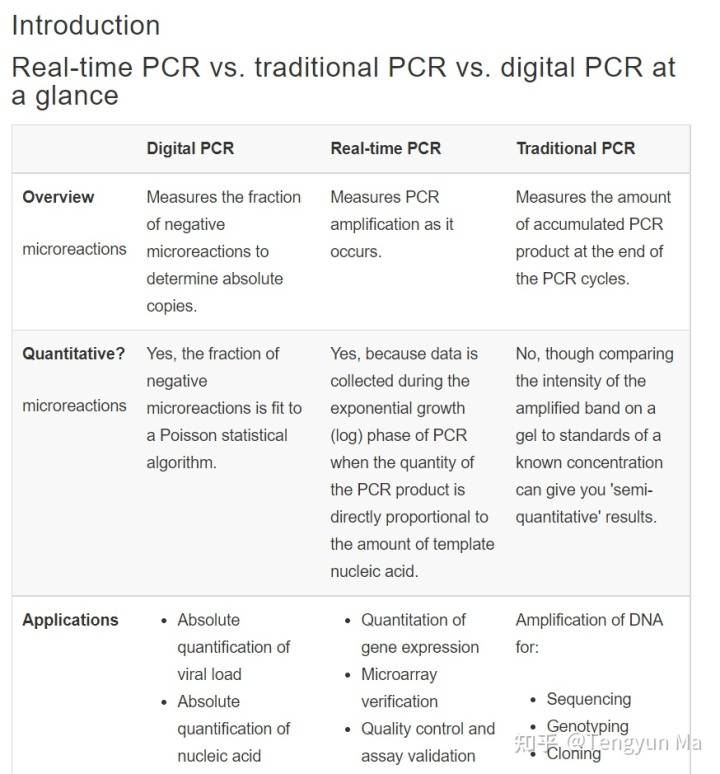
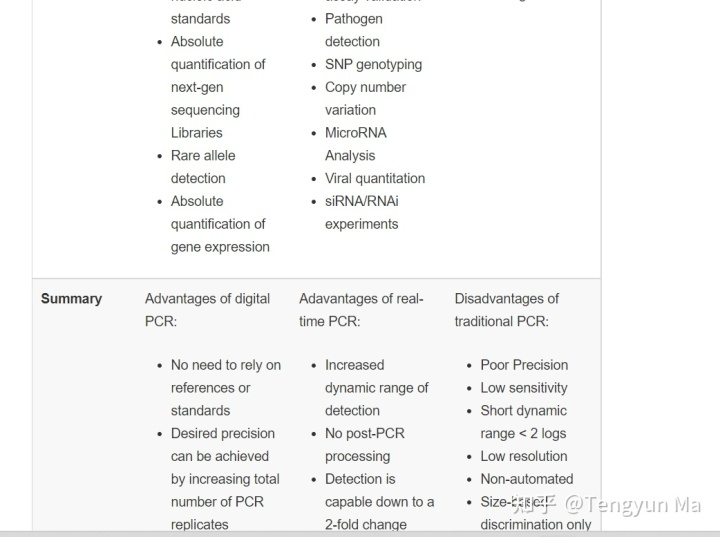
PCR and qPCR

1.称呼上,qPCR就是指实时荧光定量PCR。qPCR is commonly used to describe RT-qPCR. Similarly, RT is used to denote real-time PCR rather than reverse transcription。
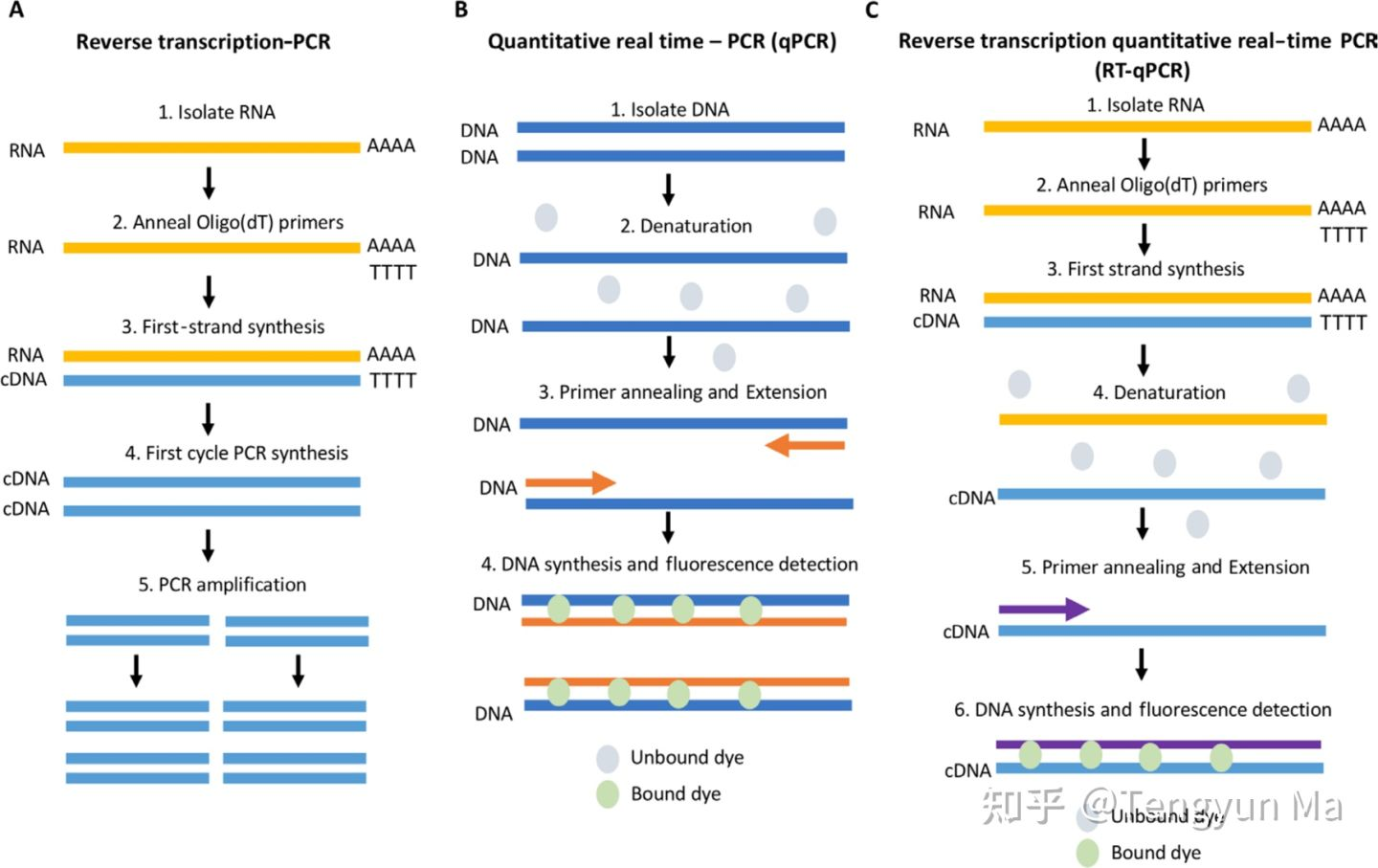
Schematic comparing RT-PCR, qPCR and RT-qPCR. (A) RT-PCR workflow. RNA is isolated and cDNA is generated via reverse transcription (RT); PCR is then carried out to amplify areas of interest. (B) qPCR schematic. DNA is isolated and amplified; amplification is quantitated using a p
One of the most common uses of qPCR is determining the copy number of a DNA sequence of interest. Using absolute quantitation, the user is able to determine the target copy numbers in reference to a standard curve of defined concentration in a far more accurate way than ever before. RT-qPCR, on the other hand, allows the investigation of gene expression changes upon treatment of model systems with inhibitors, stimulants, small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) or knockout models, etc. This technique is also routinely used to detect changes in expression both prior to (as quality control) and after (confirmation of change) RNA-Seq experiments.
实时定量PCR,指的是PCR过程中每个循环都有数据的实时记录,因此可以对起始模板数量进行精确的分析。
real time RT-PCR指的是 qPCR+RT-PCR的组合,是说将mRNA逆转录为cDNA后再作为模板进行实时荧光PCR分析,因为RT-PCR是可以定性的,但不能进行定量检测的。实时荧光定量PCR不仅可以用cDNA作为模板,也可以用基因组DNA等作为模板

2.The most crucial step in the qPCR and RT-qPCR pipeline is arguably sample isolation.Most often, extraction is carried out using commercially available kits. In addition to extraction considerations, it is essential that RNA is not contaminated with DNA, since this cannot be distinguished from cDNA in the qPCR reaction.
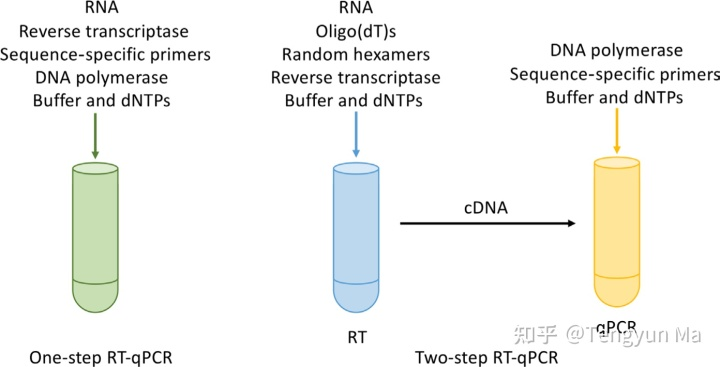
One-step vs two-step RT-qPCR. One-step RT-qPCR involves the generation of cDNA via reverse transcription and qPCR amplification of the target sequence in one reaction. Two-step RT-qPCR separates out the two steps (RT-PCR and qPCR), thus enabling more target sequences to be analys
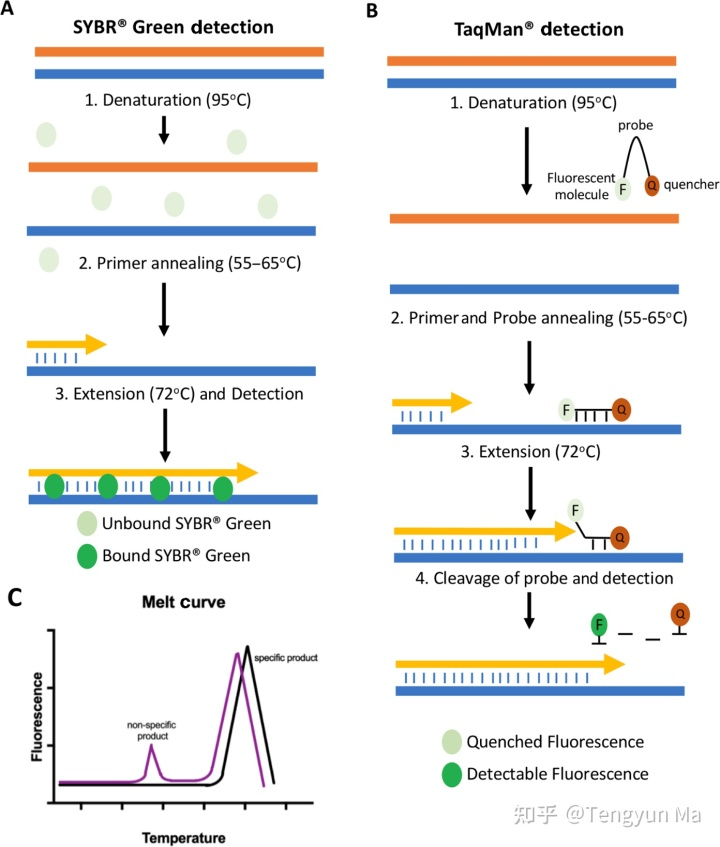
3.Detection methods
4.Real-time detection of the qPCR cycle results in an amplification curve with initiation, exponential and plateau phases (Figure 5A). This curve forms the basis of quantitation. When amplification starts, the level of fluorescence is low and is used to set the baseline level of fluorescence. As the reaction progresses into the exponential growth, fluorescence reaches a level which is significantly higher than the baseline; this is referred to as the threshold level. The threshold level is the heart of quantitation, as the point at which your sample crosses this threshold is recorded as the Ct or Cq value. The threshold is set in the exponential phase, so the reading is not affected by reagent shortages, etc. in the plateau phase. The second crucial factor in quantitation is the use of a reference gene (RG), an endogenous control present in all samples at a consistent concentration which does not change in response to biological conditions. Often, genes such as GAPDH and β-actin are used; however, the levels of these transcripts can change in certain conditions, thus it is essential that the RGs are matched to the experiment.
5.RT-PCR has been used to detect the viruses responsible for respiratory infections in public health for many years. With the recent outbreak of SARS-CoV-2, the virus causing Covid-19, the use of real-time RT-PCR has come to the forefront of research.The most common test for SARS-CoV-2, which has been implemented by the World Health Organization (WHO), Public health England (PHE) and National Health Service (NHS) laboratories, is real-time RT-PCR (RT-qPCR) using a system similar to TaqMan probes.
http://link.zhihu.com/?target=https%3A//portlandpress.com/biochemist/article/42/3/48/225280/A-beginner-s-guide-to-RT-PCR-qPCR-and-RT-qPCR